
In a rapidly changing digital world, traditional software development methods often fall short. Businesses need approaches that embrace change, foster innovation, and prioritize collaboration. Adaptive Software Development (ASD) rises to this challenge.
ASD is an agile-aligned, iterative methodology designed for complex, fast-evolving software projects. It allows teams to continuously learn, adjust, and deliver high-quality software that meets user needs even as those needs shift over time.
This detailed guide covers everything you need to know about Adaptive Software Development, including its principles, life cycle, benefits, comparisons with other models, and practical use cases.
What is Adaptive Software Development (ASD)?

Adaptive Software Development (ASD) is a software development methodology focused on adaptability, collaboration, and continuous learning. It was developed by Jim Highsmith and Sam Bayer as an evolution of Rapid Application Development (RAD).
ASD helps teams handle unpredictable requirements, complex projects, and high-risk environments. Instead of rigid planning, it encourages iterative cycles and team empowerment to respond to change.
History of ASD (Adaptive Software Development)
- 1990s: ASD emerged as a response to the limitations of Waterfall and RAD.
- 1998: Jim Highsmith published "Adaptive Software Development: A Collaborative Approach to Managing Complex Systems".
- 2001: Highsmith became a co-author of the Agile Manifesto.
- Today: ASD remains a foundational methodology for modern Agile frameworks, especially in highly dynamic projects.
Need Help with Adaptive Development?
Leverage TechVerdi’s expert Software Development and Custom Software Integration services to bring your agile vision to life.
Key Characteristics of Adaptive Software Development (ASD)
Adaptive Software Development (ASD) stands out due to its unique set of characteristics that make it highly suitable for complex, fast-changing projects. Understanding these key traits helps organizations decide when and how to apply ASD effectively.
1. Mission-Focused
ASD aligns every development activity directly with the overarching business or project mission. This means the team always keeps sight of the ultimate goals and outcomes the software is meant to achieve, rather than getting lost in unnecessary details. This focus ensures that efforts deliver real value and impact.
2. Feature-Based Delivery
Rather than building large monolithic systems, ASD breaks down work into manageable feature sets or modules. Each feature delivers a usable slice of functionality, allowing early testing, feedback, and deployment.
Benefit: This incremental delivery reduces risk and helps quickly validate assumptions with real users.
3. Iterative and Timeboxed
Work in ASD is divided into short, fixed-duration cycles (often called iterations or release cycles). These cycles enable teams to deliver small increments of working software regularly.
4. Risk-Driven
ASD proactively identifies and manages risks throughout the development process. Unlike traditional methods that plan risk only upfront, ASD continuously monitors and adapts to emerging risks, such as technological uncertainty, shifting requirements, or resource availability.
Build Smarter Products with AI
Adaptive methods shine when combined with intelligent solutions. Explore our AI Development and AI Consulting services to future-proof your software.
5. Change-Tolerant
Change is considered the norm, not the exception. ASD embraces evolving requirements and adapts the development process accordingly. Teams are prepared to respond to new insights, market shifts, or customer feedback without derailing progress.
6. Collaborative Environment
Collaboration is fundamental in ASD. Teams work closely together with stakeholders, including customers, business analysts, developers, and testers. Open communication, trust, and shared ownership are encouraged to foster creativity and problem-solving.
7. Learning-Oriented
Continuous learning from each iteration is a hallmark of ASD. After every cycle, teams conduct reviews, retrospectives, and technical assessments to identify lessons learned. This knowledge is used to improve the next cycle, making the project smarter and more efficient over time.
8. Empowered Teams
ASD decentralizes decision-making, empowering teams to take ownership of their work. This autonomy accelerates responsiveness and innovation, as teams can adjust priorities and approaches without waiting for top-down directives.
9. Integrated Testing and Quality Assurance
Quality is built into every iteration with continuous integration and testing. Rather than testing only at the end, ASD encourages ongoing verification to catch defects early and ensure that software meets high standards.
10. Scalable and Flexible for Complexity
ASD can scale from small teams to large projects with multiple teams. Its emphasis on adaptability and incremental delivery helps manage the complexity of large software systems by breaking them down into manageable chunks.
Custom Web & App Solutions for Evolving Needs
Adaptive software thrives in dynamic environments. Let our Web Development and Mobile App Development teams build flexible, scalable applications.
Summary Table of Key Characteristics of Adaptive Software Development
|
Characteristic |
Description |
Benefit |
|---|---|---|
|
Mission-Focused |
Keeps development aligned to business goals |
Maximizes value delivery |
|
Feature-Based Delivery |
Builds and delivers functional features incrementally |
Early feedback and validation |
|
Iterative & Timeboxed |
Short fixed cycles for work completion |
Faster delivery and flexibility |
|
Risk-Driven |
Continuous risk identification and management |
Prevents costly delays and errors |
|
Change-Tolerant |
Welcomes evolving requirements |
Maintains relevance and agility |
|
Collaborative |
Encourages open communication among all stakeholders |
Better alignment and quality |
|
Learning-Oriented |
Emphasizes reflection and improvement each iteration |
Continuous process and product improvement |
|
Empowered Teams |
Decentralized decision-making and team ownership |
Higher motivation and innovation |
|
Integrated Testing |
Quality assurance embedded throughout development |
Early defect detection |
|
Scalable & Flexible |
Suitable for both small and large complex projects |
Effective complexity management |
Optimize Your Digital Strategy
Combine adaptive development with powerful marketing tools. Use Search Engine Optimization, Google Ads, and Social Media Marketing to drive results.
Principles of Adaptive Software Development (ASD)
Here are the 7 foundational principles of Adaptive Software Development:
Adaptability:
Plans are flexible and evolve with the project.
Collaboration:
Strong teamwork and stakeholder involvement drive progress.
Continuous Learning:
Each iteration promotes improvement.
Iterative Development:
Software is delivered in incremental cycles.
Risk Management:
Proactively identifies and addresses risks.
Quality Focus:
Continuous testing ensures software meets standards.

Turn Data into Action
Make informed adaptive decisions with Data Analytics and Natural Language Processing services.
Phases of Adaptive Software Development
ASD uses three dynamic and repeating phases that together create a continuous cycle of improvement and delivery:
1. Speculate
- Accept and acknowledge the inherent uncertainty and unpredictability of complex projects. Instead of rigid plans, develop high-level adaptive plans that provide direction but remain flexible.
- Use initial constraints, business goals, and evolving requirements to sketch out release cycles or increments, allowing room for change as new information emerges.
- Focus on setting a vision and defining the mission, rather than detailed specifications, to keep the project aligned with overall objectives.
2. Collaborate
- Build and maintain a culture of trust, transparency, and open communication among all team members and stakeholders.
- Encourage creativity and initiative within the team, allowing individuals to contribute their expertise while working toward shared goals.
- Actively gather and incorporate feedback from both the team and customers to continuously adjust the project direction and priorities in real time.
- Collaboration also includes resolving conflicts constructively and ensuring that teamwork drives progress.
3. Learn
- After each iteration or release cycle, take time to reflect on the outcomes, successes, and challenges faced during development.
- Conduct structured activities such as focus groups, technical reviews, retrospectives, and postmortems to gather insights.
- Use these learnings to improve processes, refine requirements, update plans, and enhance team skills, thus ensuring continuous growth and adaptation throughout the project lifecycle.

Got a Game Idea That Needs Iterative Building?
Our Game Development team can prototype, test, and scale your vision using ASD principles.
Adaptive Software Development vs Other Methodologies
|
Feature |
ASD |
Waterfall |
Scrum |
Kanban |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Approach |
Adaptive & iterative |
Sequential & fixed |
Iterative & sprint-based |
Continuous & flow-based |
|
Planning |
High-level & adaptive |
Detailed upfront |
Sprint planning |
Ongoing planning |
|
Customer Involvement |
Continuous |
Initial only |
Frequent reviews |
Continuous feedback |
|
Risk Management |
Continuous |
At planning phase |
Proactive |
Proactive |
|
Best Use Case |
Complex, dynamic projects |
Stable, clear projects |
Rapid delivery needs |
Continuous delivery |
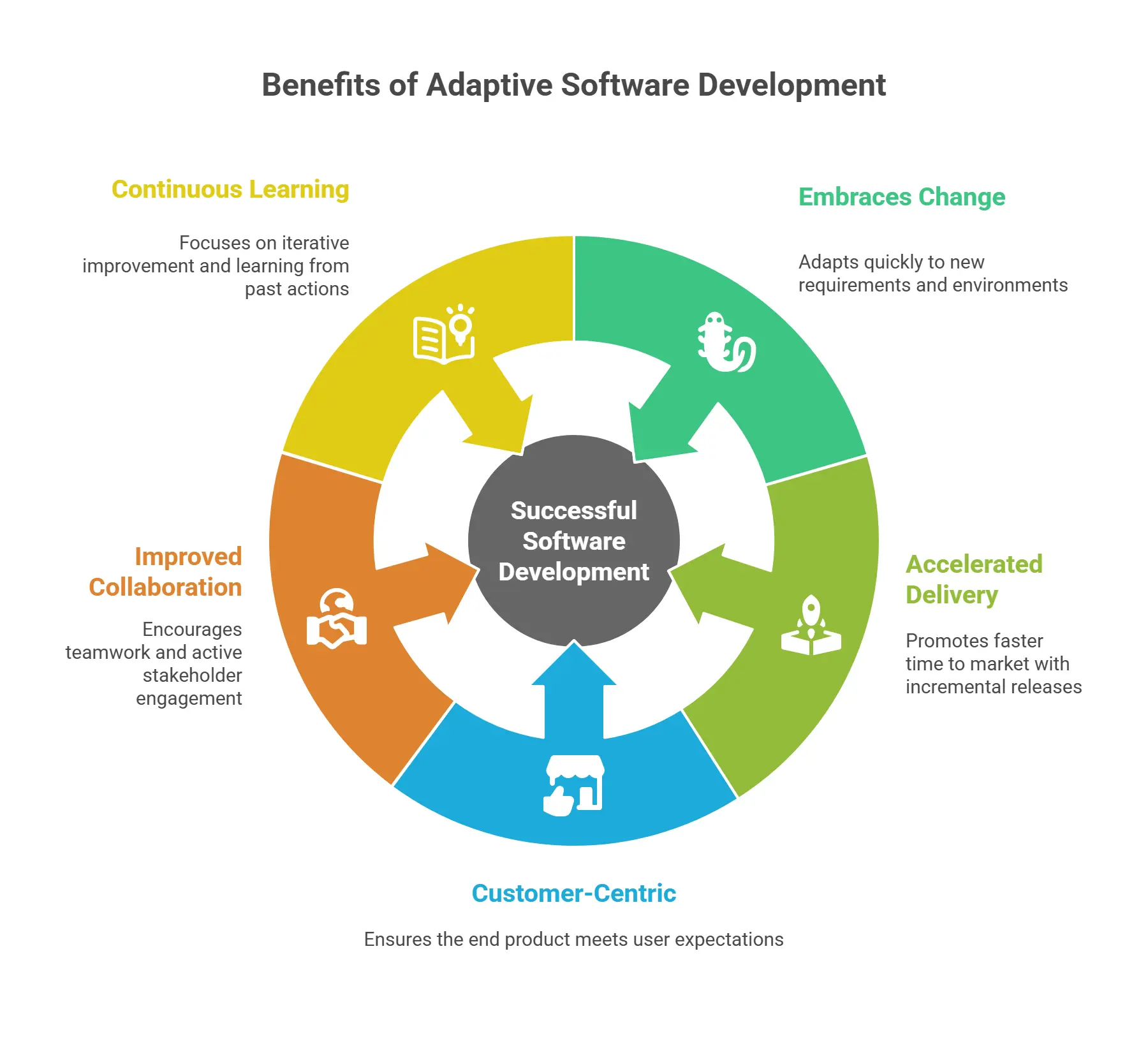
Benefits of Adaptive Software Development
Embraces Change
ASD thrives in changing environments and adapts quickly to new requirements.
Accelerated Delivery
Promotes faster time to market with incremental releases.
Customer-Centric
Regular feedback ensures the end product meets user expectations.
Improved Collaboration
Encourages teamwork and active stakeholder engagement.
Continuous Learning
Focused on iterative improvement and learning from past actions.
Seamless Integrations for Rapid Scaling
Enhance agility with CRM Solutions and Custom Software Integration built to adapt with your business.
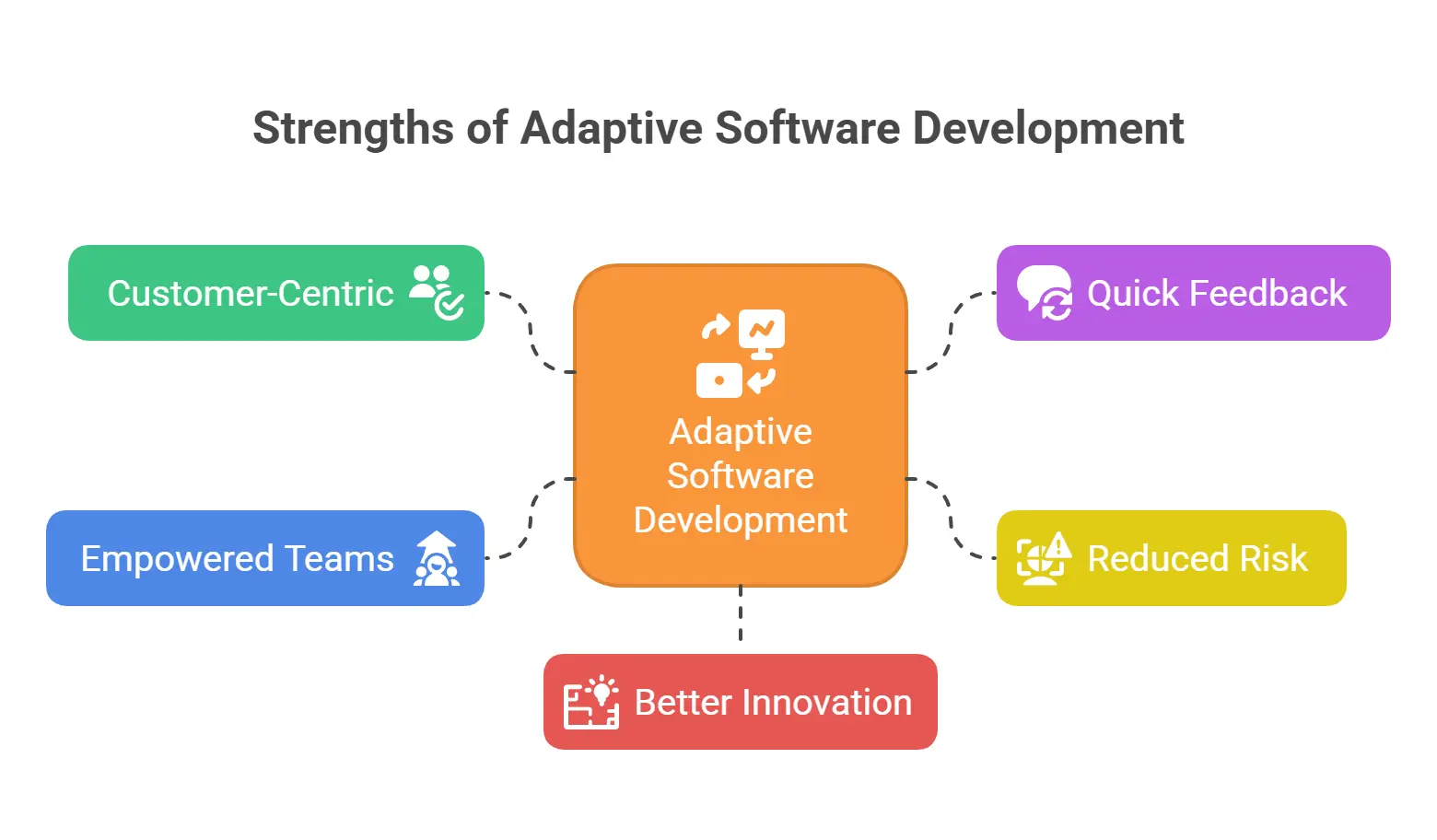
Strengths of Adaptive Software Development (ASD)
Customer-Centric:
High involvement ensures the product meets expectations.
Quick Feedback:
Iterative cycles allow fast user feedback.
Reduced Risk:
Early testing and planning minimize late-stage failures.
Empowered Teams:
Teams own their work and improve continuously.
Better Innovation:
Adaptive planning encourages creative problem-solving.
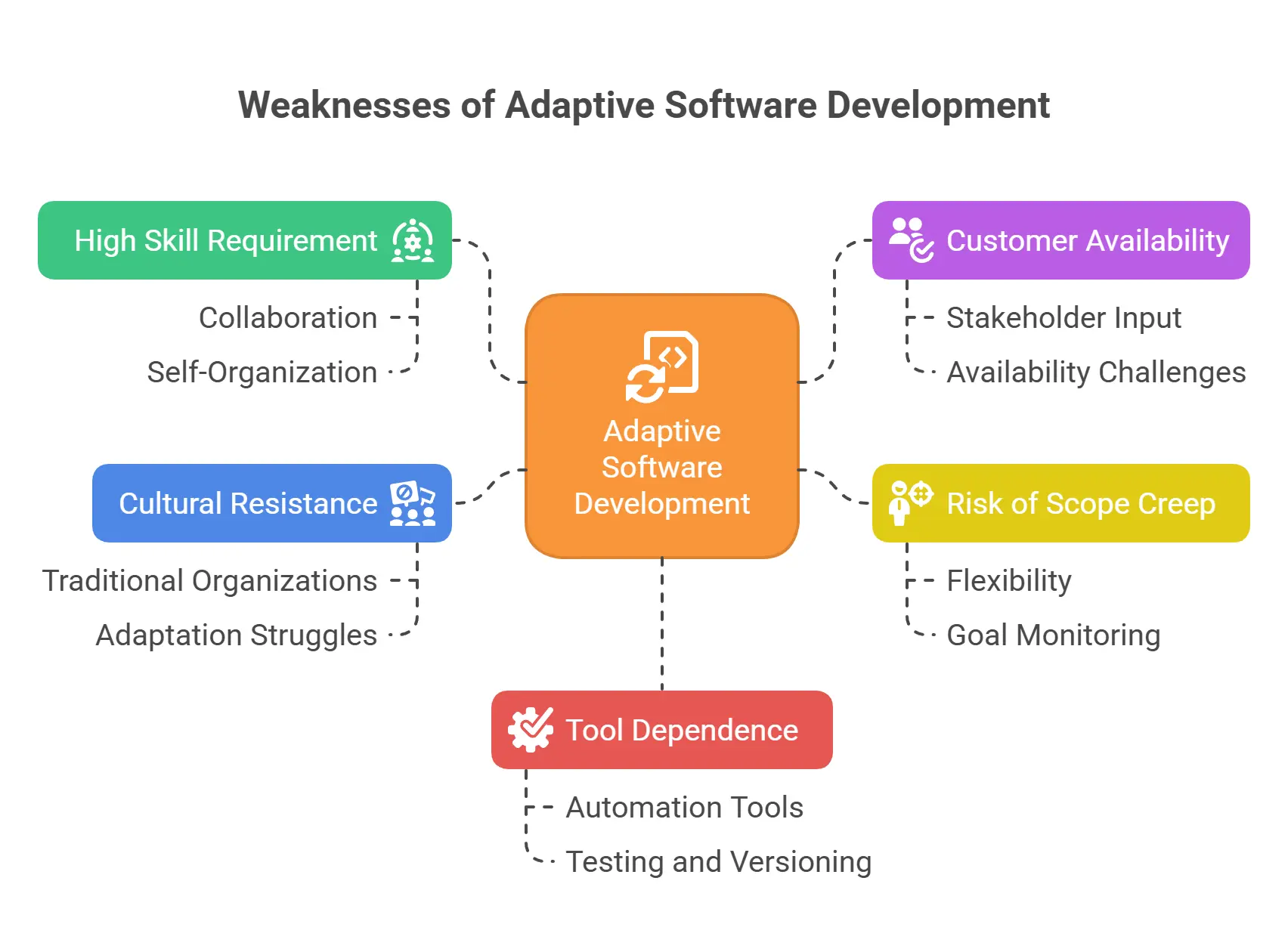
Weaknesses of Adaptive Software Development (ASD)
High Skill Requirement:
Teams need strong collaboration and self-organization skills.
Customer Availability:
Constant stakeholder input can be difficult to maintain.
Risk of Scope Creep:
Flexibility may lead to shifting goals if not monitored.
Cultural Resistance:
Traditional organizations may struggle to adapt.
Tool Dependence:
ASD benefits from automation tools for testing and versioning.
Build Adaptive Software with Confidence
Partner with TechVerdi’s Software Development experts to implement flexible, scalable solutions tailored to your business goals.
When to Use Adaptive Software Development (ASD)
You should consider ASD when:
- Requirements are likely to evolve during the project.
- The solution domain is complex or emerging.
- Stakeholders are available for ongoing collaboration.
- Quick releases and continuous improvement are priorities.
- You need to manage high-risk environments.
Challenges of Adaptive Software Development (ASD)
- Lack of structure can be overwhelming for teams used to Waterfall.
- Requires high communication and collaboration discipline.
- Can be difficult to estimate timelines or budgets accurately.
- Demands a culture of trust and adaptability.
Real-World Examples of Adaptive Software Development in Action
Example: Mobile App Development
In fast-paced startups, features often pivot based on user feedback. ASD helps teams launch quickly and iterate often.
Example: E-commerce Platforms
Online stores need to adjust to seasonal trends, customer behavior, and competitor features all ideal for ASD’s rapid feedback loop.
Adaptive Mobile Apps That Grow with You
Get dynamic, user-driven Mobile App Development using iterative and agile methods.
Conclusion
Adaptive Software Development (ASD) is a powerful methodology for managing complex, uncertain, and fast-changing software projects. It encourages continuous learning, collaboration, and iteration qualities essential in today’s digital environment.
By embracing ASD, teams can produce better software, reduce risk, and deliver ongoing value to users and stakeholders. If you’re looking for a development model that thrives on change and feedback, ASD could be the perfect fit.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Adaptive Software Development (ASD) is an iterative software development methodology focused on learning, collaboration, and flexibility in response to change.
Speculate, Collaborate, and Learn.
ASD predates Agile and influenced its formation. While Agile includes frameworks like Scrum and Kanban, ASD is its own methodology with unique phases.
Yes, especially for complex, evolving projects that require stakeholder involvement and iterative delivery.
Jim Highsmith and Sam Bayer introduced ASD in the 1990s as an evolution of Rapid Application Development.
Use ASD when:
- Requirements are unclear.
- Rapid changes are expected.
- You need fast iteration and feedback.
ASD was introduced by Jim Highsmith and Sam Bayer in the 1990s as an evolution of Rapid Application Development (RAD).
Kickstart Your Project in Just 3 Steps
Simple. Transparent. Zero pressure.
Step 1: Share Your Project Goals
Step 2: Get a Tailored Quote
Step 3: See What We’ll Build
Steps You've Completed
Need Help or Have a Question?
If you're unsure where to start or want expert guidance, our team is just a message away.
Talk to Our ExpertGet Expert AI & Tech Guidance
Need help implementing adaptive methods? Our AI Consulting and LLM Solutions can guide your roadmap
